In the realm of technology, CS 498 Cloud Computing Applications stand tall as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way we access, store, and process data. From personal use to enterprise-level operations, cloud computing applications are reshaping the digital landscape, offering a myriad of benefits and unlocking new possibilities.
As we delve into the depths of this topic, we’ll explore the intricacies of cloud computing services, unravel the architecture behind these applications, and delve into the security measures that safeguard their integrity. We’ll also uncover the latest trends shaping the future of cloud computing and examine how it’s empowering businesses to operate with unprecedented efficiency and agility.
Cloud Computing Applications
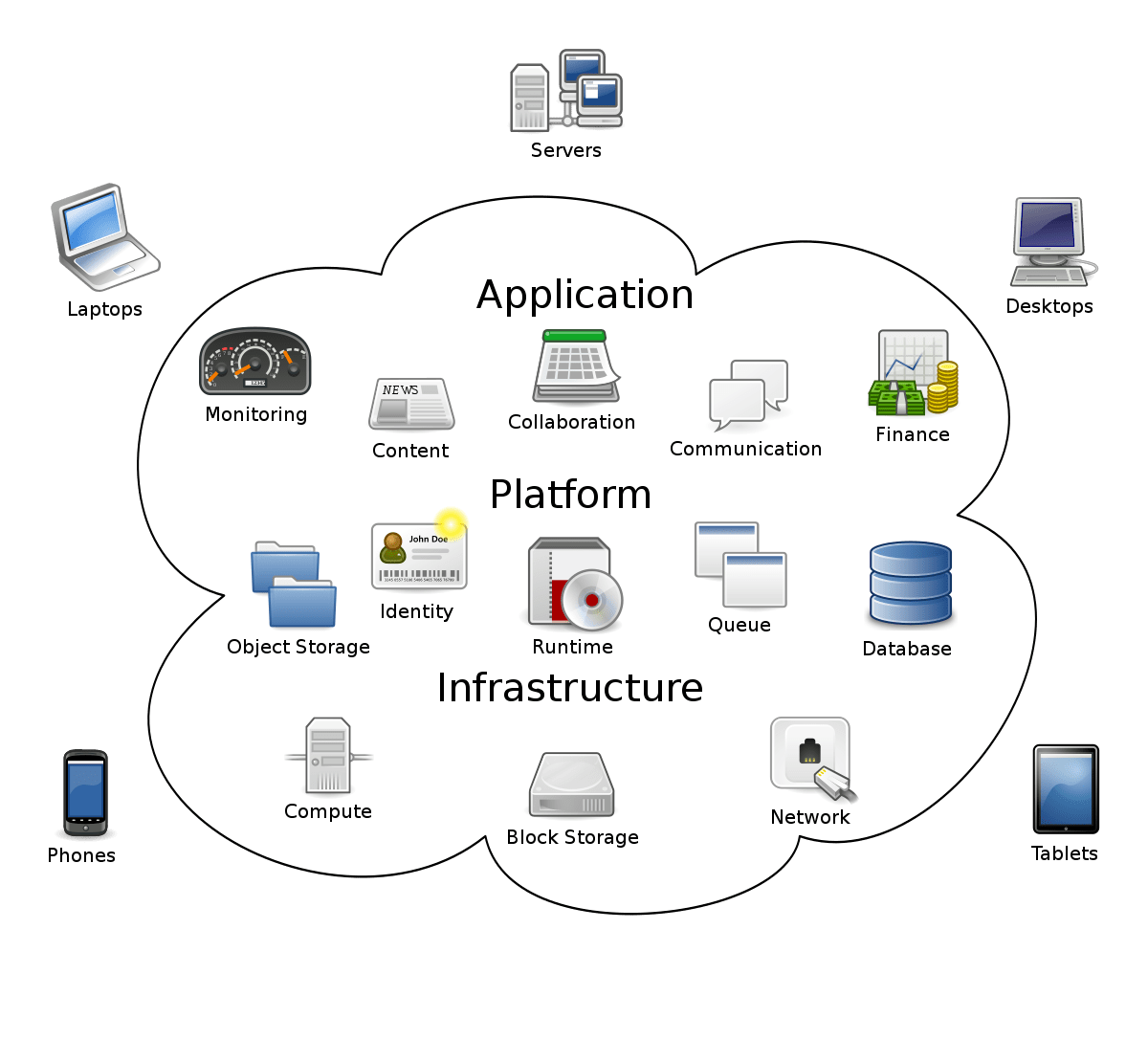
Cloud computing applications are software programs that run on cloud computing platforms. These platforms provide access to shared computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. Cloud computing applications can be used for a wide variety of purposes, including data storage and processing, web hosting, and software development.
Some examples of cloud computing applications include:
- Google Drive:A cloud storage and file sharing service.
- Microsoft Office 365:A cloud-based productivity suite that includes applications such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- Salesforce:A cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) system.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):A cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services, such as computing, storage, and networking.
- Microsoft Azure:A cloud computing platform that provides a similar range of services to AWS.
There are many benefits to using cloud computing applications. These benefits include:
- Cost savings:Cloud computing applications can be more cost-effective than traditional software applications, as they eliminate the need for businesses to purchase and maintain their own hardware and software.
- Scalability:Cloud computing applications can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs.
- Reliability:Cloud computing applications are typically more reliable than traditional software applications, as they are hosted on redundant servers.
- Security:Cloud computing applications are typically more secure than traditional software applications, as they are hosted in secure data centers.
- Accessibility:Cloud computing applications can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are offered in three primary models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model provides a different level of control and responsibility to the user.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provides access to fundamental computing resources such as servers, storage, and networks.
- Users have full control over the underlying infrastructure, including the operating system and applications.
- Suitable for organizations with specialized IT requirements and the expertise to manage their own infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS), Cs 498 cloud computing applications
- Offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications.
- Provides pre-configured infrastructure and development tools, simplifying application development and deployment.
- Suitable for organizations that want to focus on application development without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Provides access to ready-to-use software applications over the internet.
- Users can access the applications without installing or managing the software on their own systems.
- Suitable for organizations that need access to specific software applications without investing in their own infrastructure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cloud Computing Service
- Business Requirements:Identify the specific needs and objectives of the organization.
- Control and Flexibility:Determine the level of control and flexibility required over the infrastructure and applications.
- Cost and Scalability:Consider the cost of the service and its ability to scale as the organization grows.
- Security and Compliance:Ensure that the service meets the organization’s security and compliance requirements.
- Provider Reliability and Support:Evaluate the reliability and support offered by the cloud service provider.
Cloud Computing Architecture: Cs 498 Cloud Computing Applications
Cloud computing architecture encompasses the various components and their interrelationships within a cloud computing system. It defines the overall structure and organization of the cloud environment, including its physical and logical elements.
Components of Cloud Computing Architecture
- Front-end:The user-facing component that provides the interface and services to end-users, such as web browsers or mobile apps.
- Back-end:The infrastructure that supports the front-end and manages the underlying resources, such as servers, storage, and networks.
- Cloud Middleware:Software that connects the front-end and back-end, managing communication, data transfer, and security.
- Cloud Management Tools:Interfaces and tools used to manage and monitor the cloud environment, including provisioning, scaling, and performance optimization.
- Network Infrastructure:The network connections and protocols that enable communication between the various components of the cloud architecture.
Cloud Computing Security
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, but it also presents unique security challenges. Understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures are crucial for protecting cloud computing applications and data.
Security risks associated with cloud computing include:
- Data breaches:Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored in the cloud can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liability.
- Denial of service (DoS) attacks:Overwhelming cloud-based services with excessive traffic can disrupt operations and cause downtime.
- Malware:Malicious software can infect cloud-based systems, compromising data and disrupting services.
- Insider threats:Employees with access to cloud-based systems can pose a security risk through malicious or unintentional actions.
Security Measures for Cloud Computing Applications
To protect cloud computing applications, organizations should implement comprehensive security measures, including:
- Encryption:Encrypting data at rest and in transit ensures its confidentiality.
- Access controls:Implementing strong access controls, such as role-based access control (RBAC), limits access to data and resources to authorized users.
- Firewalls:Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access to cloud-based systems.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS):These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert on potential threats.
- Regular security audits:Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and improve the overall security posture.
Best Practices for Cloud Computing Security
In addition to implementing security measures, organizations should adopt best practices for cloud computing security, such as:
- Shared responsibility model:Understanding the shared responsibility model and collaborating with cloud providers on security.
- Data backup and recovery:Implementing robust data backup and recovery strategies to protect against data loss.
- Security awareness training:Educating employees on cloud computing security risks and best practices.
- Incident response plan:Developing and practicing an incident response plan to respond effectively to security breaches.
- Continuous monitoring:Regularly monitoring cloud-based systems for security threats and vulnerabilities.
Cloud Computing Trends
Cloud computing is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of cloud computing and the way businesses operate.
One of the most significant trends in cloud computing is the increasing adoption of hybrid cloud models. Hybrid cloud models combine public and private clouds to provide businesses with the best of both worlds. Public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, while private clouds offer security and control.
Another major trend is the rise of serverless computing. Serverless computing allows businesses to develop and deploy applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure. This can significantly reduce the cost and complexity of developing and operating applications.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage resources closer to the devices and sensors that generate and consume data. This reduces latency and improves performance for applications that require real-time data processing.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are increasingly being used in cloud computing to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide personalized experiences. For example, AI can be used to analyze customer data to identify trends and patterns, or to automate the process of customer support.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a new type of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize many industries, including cloud computing. For example, quantum computing could be used to develop new algorithms for solving complex problems or to create new types of cloud-based applications.
These are just a few of the trends that are shaping the future of cloud computing. As cloud computing continues to evolve, it will become increasingly important for businesses to understand these trends and how they can be used to improve their operations.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key benefits of using cloud computing applications?
Cloud computing applications offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, increased flexibility, enhanced collaboration, improved security, and access to cutting-edge technologies.
How do I choose the right cloud computing service for my needs?
Consider factors such as the type of application, data storage requirements, security measures, scalability, and cost when selecting a cloud computing service.
What are the common security risks associated with cloud computing?
Potential security risks include data breaches, unauthorized access, malware attacks, and denial-of-service attacks. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to mitigate these risks.