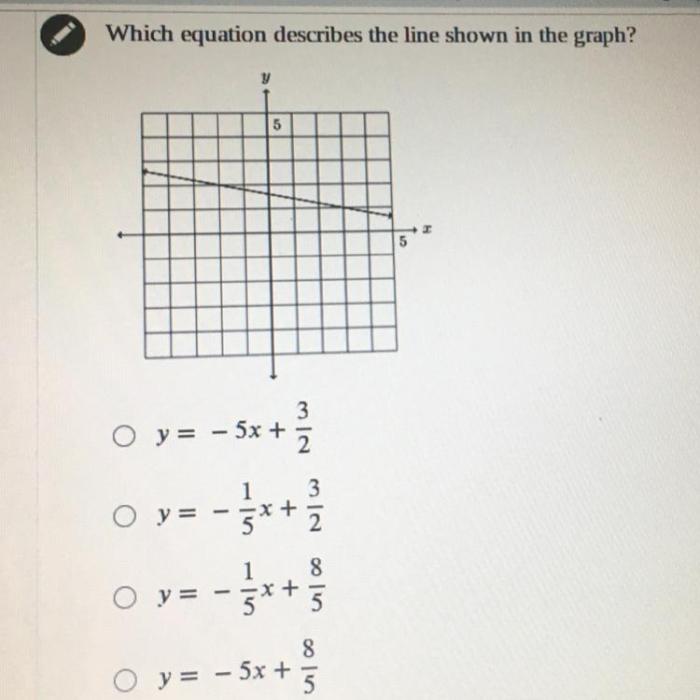
Which equation describes this line – Embarking on a journey to unravel the enigmatic equation that governs a line, this exploration delves into the captivating world of linear equations, where the relationship between points and slopes unravels.
Unveiling the diverse forms of line equations, from the familiar slope-intercept to the intricate point-slope and standard forms, this discourse provides a comprehensive understanding of the mathematical underpinnings of linear functions.
1. Line Equation Overview
A line equation is a mathematical representation of a straight line. It describes the relationship between the x and y coordinates of any point on the line. There are several different forms of line equations, each with its own advantages and applications.
The most common forms of line equations are:
- Slope-intercept form: y = mx + b
- Point-slope form: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
- Standard form: Ax + By = C
2. Identifying Line Equations
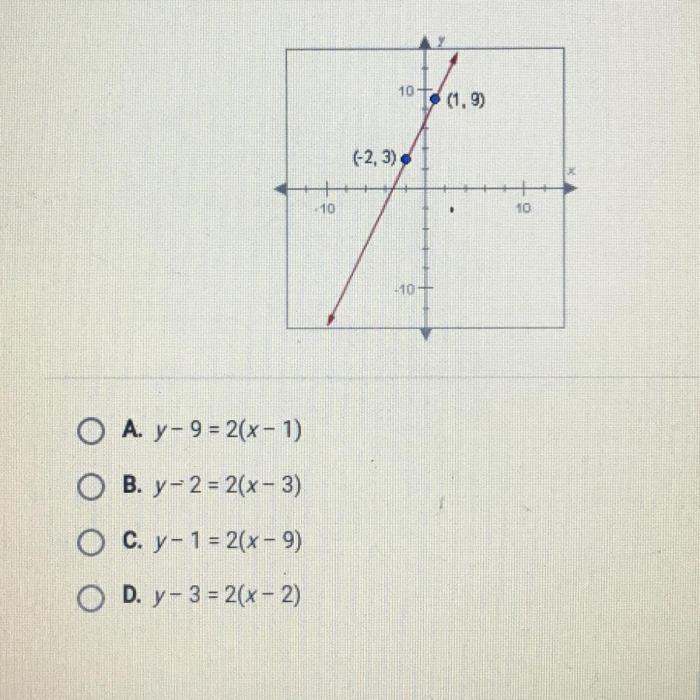
To determine the equation of a line given a graph, follow these steps:
- Identify two points on the line.
- Calculate the slope (m) using the formula: m = (y2
- y1) / (x2
- x1)
- Choose one of the points and substitute its coordinates and the slope into the point-slope form: y
- y1 = m(x
- x1)
- Simplify the equation to get the slope-intercept form: y = mx + b
To convert between different forms of line equations, use the following steps:
- Slope-intercept to point-slope: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
- Point-slope to slope-intercept: y = mx + (y1 – mx1)
- Slope-intercept to standard: Ax + By = C (where A = m, B = -1, C = b)
- Standard to slope-intercept: y = (-A/B)x + (C/B)
3. Applications of Line Equations: Which Equation Describes This Line
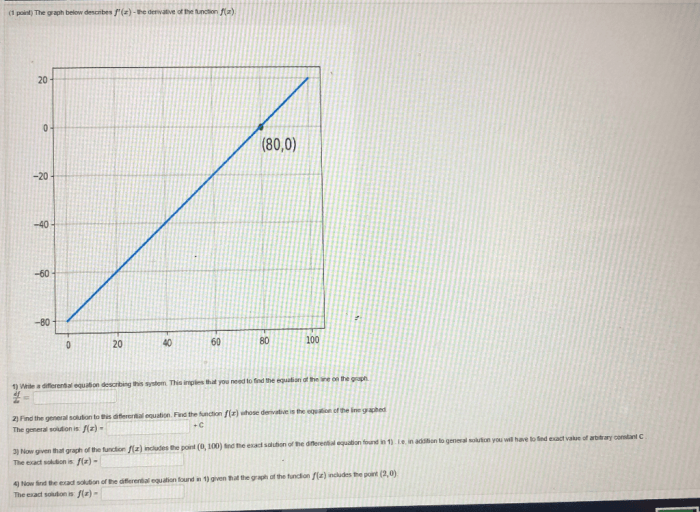
Line equations have numerous applications in real-world scenarios:
- Physics: Describing motion, forces, and trajectories
- Engineering: Designing bridges, buildings, and machines
- Economics: Modeling supply and demand curves, forecasting financial trends
- Computer graphics: Creating 3D objects and animations
- Medicine: Analyzing patient data, diagnosing diseases
4. Advanced Line Equation Analysis
Line equations can be analyzed to determine various properties:
- Slope: Indicates the steepness and direction of the line
- Y-intercept: The point where the line crosses the y-axis
- Parallelism: Two lines are parallel if they have the same slope
- Perpendicularity: Two lines are perpendicular if their slopes are negative reciprocals of each other
Line equations can also be manipulated to solve complex problems:
- Finding intersections: Solving systems of linear equations to determine where two lines cross
- Calculating distances: Using the distance formula to find the distance between a point and a line
- Transformations: Applying translations, rotations, and reflections to manipulate lines
FAQ Guide
What is a line equation?
A line equation is a mathematical expression that describes the relationship between the coordinates of points on a line.
How do I determine the equation of a line from a graph?
To determine the equation of a line from a graph, identify two points on the line and use the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
What are the different forms of line equations?
The three main forms of line equations are slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), point-slope form (y – y1 = m(x – x1)), and standard form (Ax + By = C).