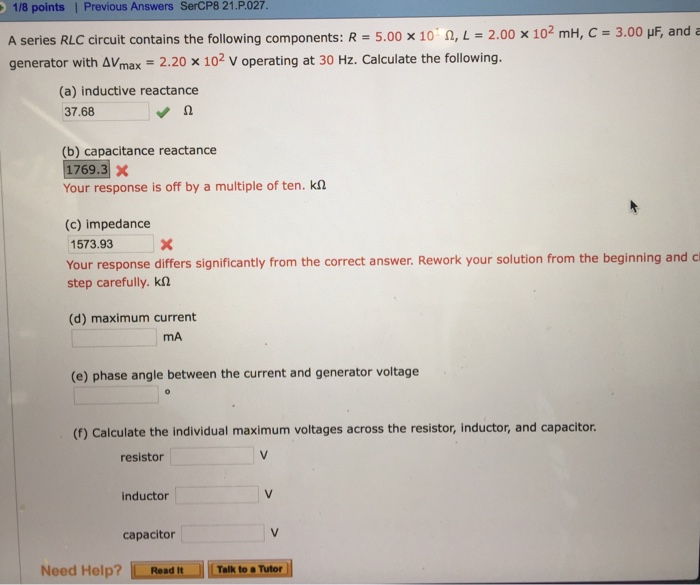
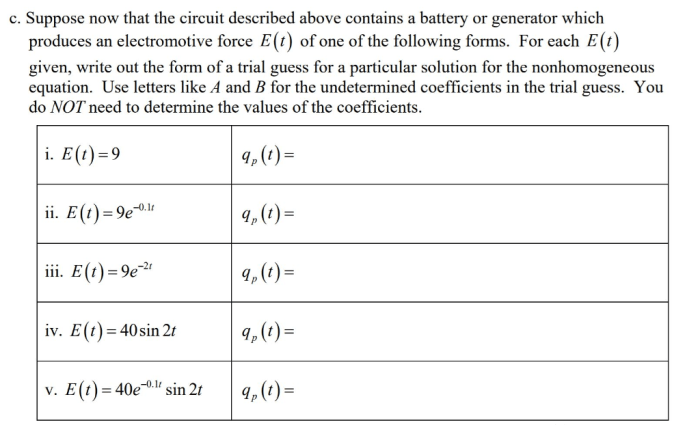
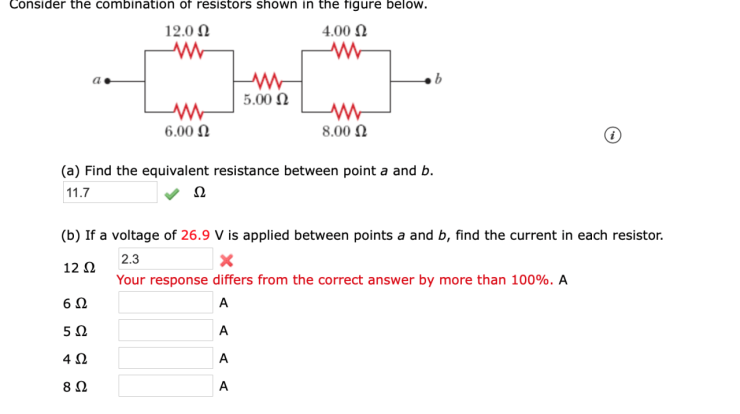
A series circuit contains a generator, resistors, and other components, forming a closed loop that allows electrical current to flow. This arrangement plays a crucial role in various applications, from simple lighting circuits to complex electronic devices. Understanding the behavior of a series circuit is essential for electrical engineers and hobbyists alike.
In a series circuit, the current flowing through each component is the same, while the voltage drop across each component adds up to the total voltage supplied by the generator. This simple yet fundamental concept forms the basis for analyzing and designing electrical circuits.
Electrical Circuit Components: A Series Circuit Contains A Generator
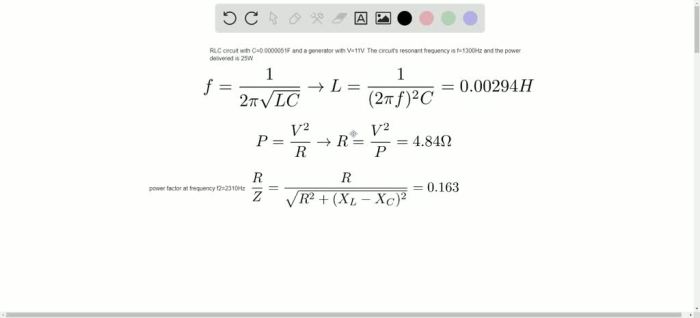
A series circuit is a type of electrical circuit in which the components are connected one after the other in a single loop. This means that the current flowing through each component is the same, and the voltage across each component is added together to give the total voltage across the circuit.
The main components of a series circuit are a generator, resistors, and other components such as capacitors and inductors. The generator is responsible for providing the electrical energy to the circuit, and the resistors are used to control the flow of current.
Other components can be used to modify the behavior of the circuit, such as capacitors to store energy or inductors to oppose changes in current.
Circuit Analysis, A series circuit contains a generator
Circuit analysis is the process of determining the current, voltage, and power in a circuit. This can be done using a variety of methods, including Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, and nodal analysis.
Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage across the resistor. Kirchhoff’s laws are two conservation laws that can be used to analyze circuits. Nodal analysis is a method of circuit analysis that uses the concept of nodes to determine the voltage at each node in the circuit.
Circuit Design
Circuit design is the process of creating a circuit that meets specific requirements. This involves selecting the appropriate components and arranging them in a way that will achieve the desired results.
When designing a circuit, it is important to consider factors such as the power requirements, the efficiency, and the cost. It is also important to make sure that the circuit is safe and reliable.
Applications of Series Circuits
Series circuits are used in a wide variety of applications, including power distribution, lighting, and electronics. In power distribution, series circuits are used to connect homes and businesses to the power grid. In lighting, series circuits are used to connect light bulbs in a string.
In electronics, series circuits are used to create a variety of electronic devices, such as radios and computers.
Series circuits have a number of advantages, including simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency. However, they also have some limitations, such as the fact that the current flowing through the circuit is the same for all components.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a generator in a series circuit?
A generator in a series circuit provides the electromotive force (EMF) that drives the current flow. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, maintaining a potential difference across the circuit.
How does the resistance of a resistor affect the current flow in a series circuit?
The resistance of a resistor impedes the flow of current. As resistance increases, the current flowing through the circuit decreases, following Ohm’s law.
What is the significance of voltage drop in a series circuit?
Voltage drop refers to the decrease in voltage across each component in a series circuit. The sum of these voltage drops equals the total voltage supplied by the generator, providing a valuable insight into the distribution of electrical energy within the circuit.