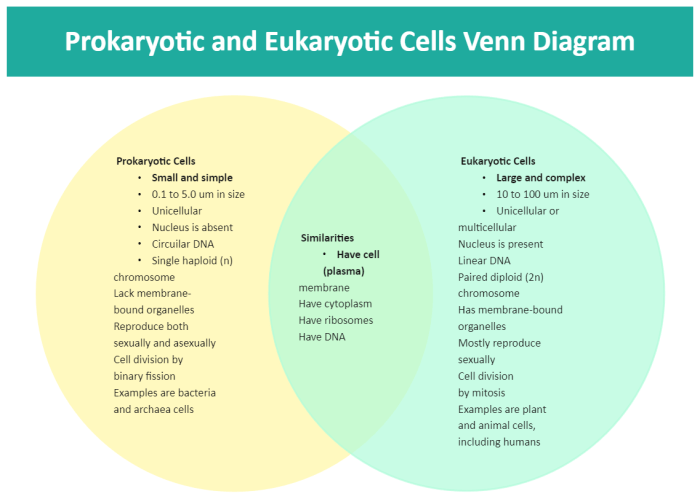
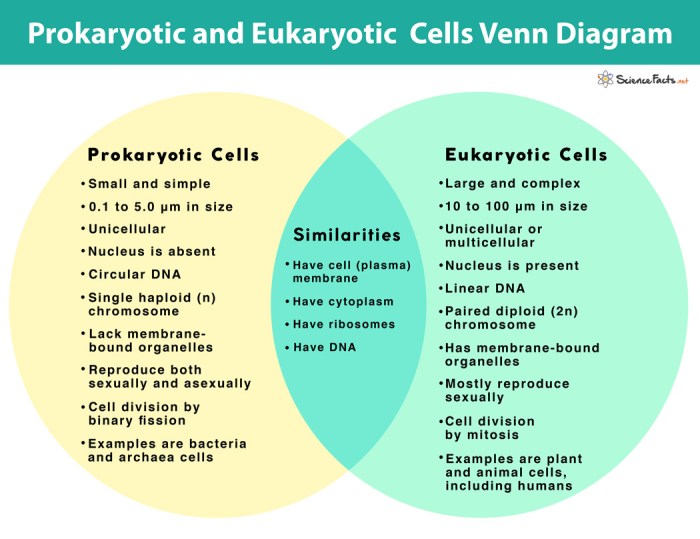
The Venn diagram eukaryotes and prokaryotes is a powerful tool for understanding the similarities and differences between these two fundamental cell types. By visually representing their defining characteristics, this diagram provides insights into their evolutionary relationships and the fundamental principles of cell biology.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the structure of a Venn diagram comparing eukaryotes and prokaryotes, explore their unique and shared characteristics, and discuss the evolutionary implications of their similarities and differences.
Venn Diagram: Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes: Venn Diagram Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes
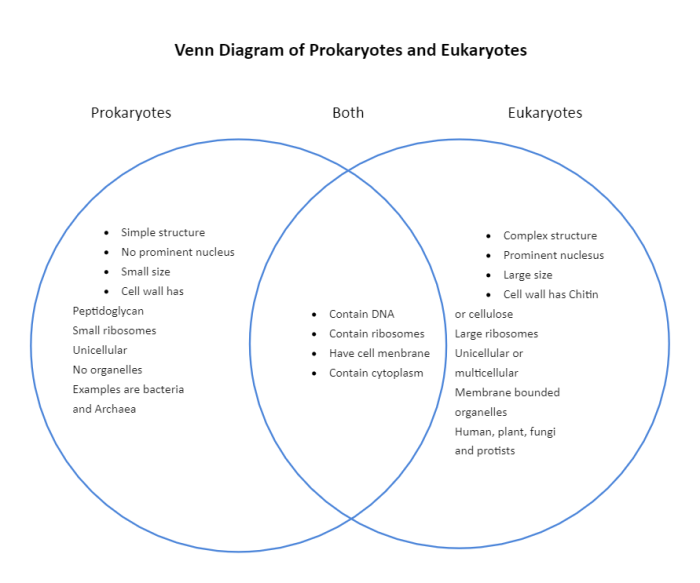
A Venn diagram is a visual tool used to compare and contrast two or more sets of data. In biology, Venn diagrams are often used to compare the characteristics of different cell types, such as eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Venn diagrams can help to illustrate the similarities and differences between two sets of data, and can be used to identify shared and unique features.
Venn Diagram Structure
A Venn diagram consists of two or more overlapping circles, with each circle representing a different set of data. The area where the circles overlap represents the similarities between the two sets of data, while the areas outside the overlap represent the unique features of each set.
In the case of eukaryotes and prokaryotes, a Venn diagram can be used to compare the characteristics of these two cell types. The circles can be labeled “Eukaryotes” and “Prokaryotes”, and the overlapping area can be used to represent the characteristics that are shared by both cell types.
Eukaryotic Characteristics
Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotes, and they have a more complex genetic structure.
- Have a nucleus
- Have membrane-bound organelles
- Are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotes
- Have a more complex genetic structure
Prokaryotic Characteristics, Venn diagram eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotes, and they have a simpler genetic structure.
- Lack a nucleus
- Lack membrane-bound organelles
- Are typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotes
- Have a simpler genetic structure
Shared Features
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes share some common characteristics, such as:
- A cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Ribosomes
- DNA
Evolutionary Implications
The similarities and differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes can be used to infer their evolutionary relationships. It is thought that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes, and that the nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles evolved as a result of a process called endosymbiosis.
The Venn diagram can be used to illustrate the evolutionary relationships between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The overlapping area of the Venn diagram represents the shared characteristics between the two cell types, while the areas outside the overlap represent the unique features of each cell type.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of a Venn diagram in comparing eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
A Venn diagram allows for a visual representation of the similarities and differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes, making it easier to identify and compare their key characteristics.
What are the main characteristics that distinguish eukaryotes from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes are distinguished from prokaryotes by the presence of a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and a more complex cellular structure.
How does the Venn diagram illustrate the evolutionary relationships between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
The Venn diagram can show the shared characteristics between eukaryotes and prokaryotes, suggesting a common ancestor, and the unique characteristics that have evolved in each lineage.