Embarking on a scientific odyssey with Bioflix Activity: Gas Exchange — Path of Air, this exploration unveils the intricate mechanisms that govern the exchange of life-sustaining gases within our bodies. Prepare to traverse the respiratory system’s labyrinthine pathways, deciphering the roles of each component in this vital process.
Our journey commences with the nasal cavity, where air embarks on its odyssey. We’ll venture through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi, witnessing the progressive refinement of air as it approaches the lungs. Finally, we’ll delve into the alveoli, the microscopic powerhouses where gas exchange occurs.
Path of Air
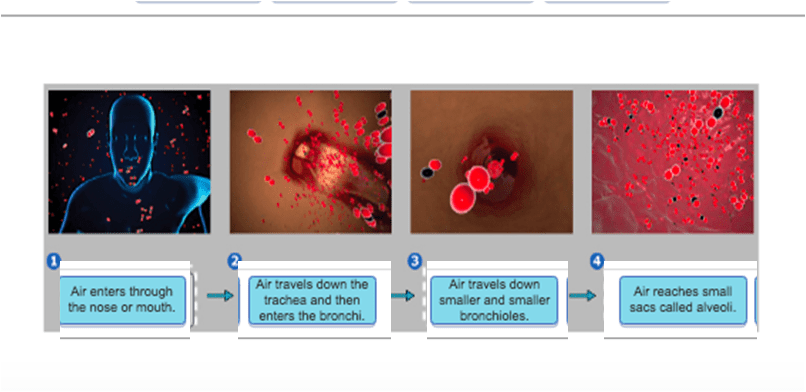
Air enters the respiratory system through the nasal cavity, which is lined with mucous membranes that trap dust and other particles. The air then passes through the pharynx, which is the back of the throat, and into the larynx, or voice box.
From the larynx, the air travels down the trachea, or windpipe, which divides into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles, which eventually lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Gas Exchange in the Lungs
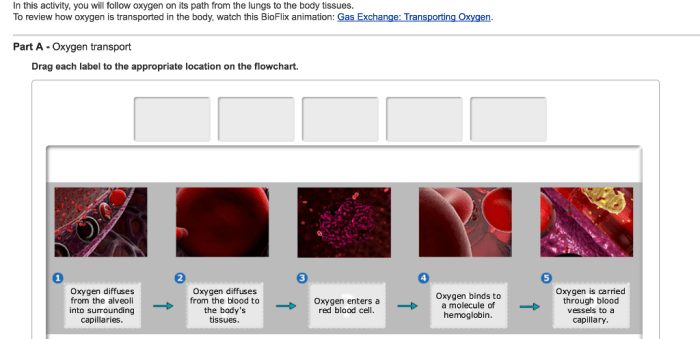
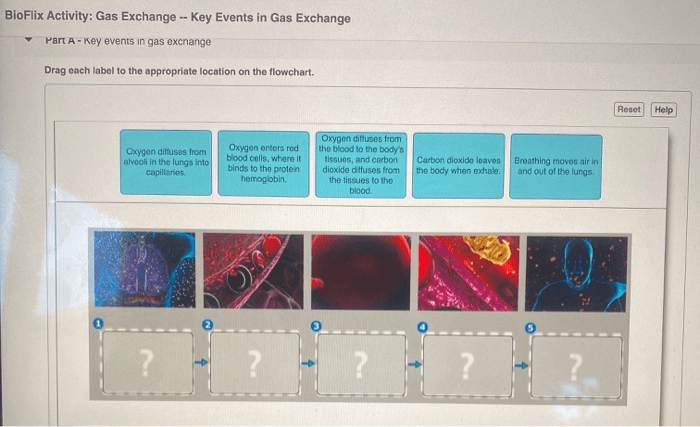
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. Oxygen from the air diffuses across the thin walls of the alveoli and into the capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli. The oxygen-rich blood is then carried away from the lungs by the pulmonary veins, while the carbon dioxide-rich blood is carried away by the pulmonary arteries.
Regulation of Breathing

Breathing is regulated by the respiratory center in the brainstem, which responds to changes in the pH and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. When the pH of the blood decreases or the carbon dioxide levels increase, the respiratory center sends signals to the muscles of the diaphragm and rib cage, causing them to contract and expand the lungs, which increases the rate and depth of breathing.
Impact of Exercise on Gas Exchange: Bioflix Activity: Gas Exchange — Path Of Air
Exercise increases the demand for oxygen, which causes the body to increase ventilation and oxygen consumption. The increased ventilation is caused by an increase in the rate and depth of breathing, while the increased oxygen consumption is caused by an increase in the number of capillaries in the alveoli and an increase in the rate of diffusion of oxygen across the alveolar walls.
Respiratory Disorders
Common respiratory disorders include asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways that causes wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi that causes coughing and shortness of breath. Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that causes the alveoli to lose their elasticity, which makes it difficult to breathe.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of the nasal cavity in gas exchange?
The nasal cavity serves as the initial entry point for air, filtering and warming it before it reaches the lungs.
How do the alveoli facilitate gas exchange?
The alveoli’s thin walls and extensive surface area allow for efficient diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the bloodstream.