A furnace equipped with a secondary heat exchanger. – Secondary heat exchangers in furnaces offer a range of benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced comfort. This comprehensive guide delves into the purpose, design, installation, maintenance, performance evaluation, and future trends of secondary heat exchangers, providing valuable insights for homeowners, contractors, and industry professionals alike.
Overview of Secondary Heat Exchangers in Furnaces

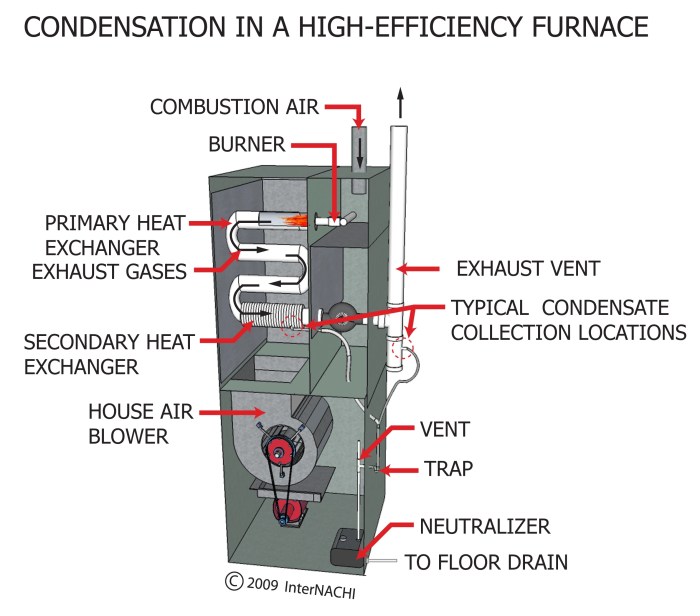
Secondary heat exchangers (SHEs) are devices installed in furnaces to enhance heat transfer and energy efficiency. They capture waste heat from the furnace’s exhaust gases and transfer it to the incoming combustion air, preheating it before it enters the combustion chamber.
Benefits of SHEs include:
- Increased thermal efficiency, reducing fuel consumption
- Lower emissions by reducing the amount of unburned fuel in the exhaust
- Improved furnace performance and longevity
Different types of SHEs include:
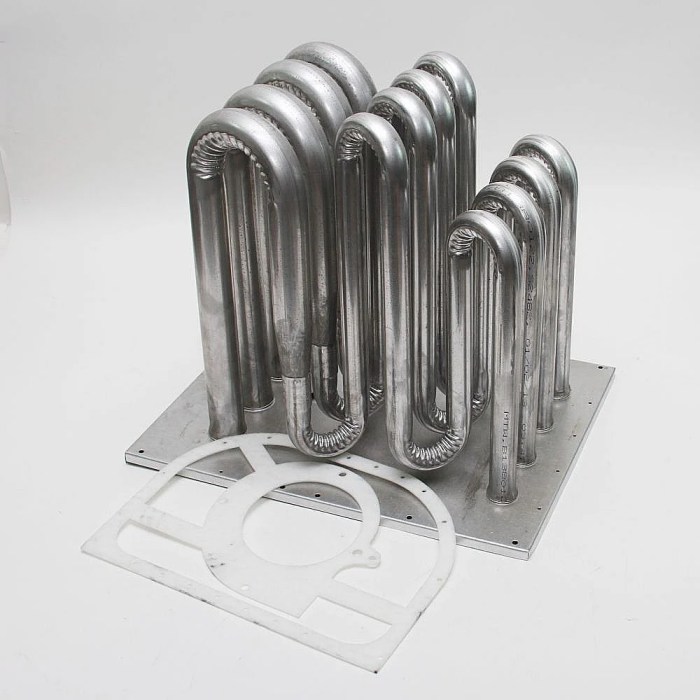
- Tubular SHEs: Consisting of a series of tubes through which exhaust gases pass, transferring heat to the surrounding air
- Plate-fin SHEs: Composed of alternating layers of plates and fins, providing a large surface area for heat transfer
- Regenerative SHEs: Utilizing a rotating matrix that alternately absorbs heat from the exhaust gases and releases it to the combustion air
Design Considerations for Secondary Heat Exchangers
The design of a SHE is influenced by factors such as:
- Material selection: Materials must withstand high temperatures and corrosion from exhaust gases
- Size and shape: Determined by the desired heat transfer rate and furnace space constraints
- Airflow optimization: Ensuring proper airflow through the SHE to maximize heat transfer
- Heat transfer efficiency: Selecting materials and designs that facilitate efficient heat transfer
Installation and Maintenance of Secondary Heat Exchangers

Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for SHE performance.
- Installation:
- Ensure a secure and airtight fit
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions for proper positioning and orientation
- Maintenance:
- Regular cleaning to remove soot and debris
- Inspection for leaks or damage
- Replacement of worn or damaged components
- Thermal efficiency: The ratio of heat transferred to the combustion air to the heat available in the exhaust gases
- Pressure drop: The reduction in pressure of the combustion air as it passes through the SHE
- Fouling factor: A measure of the accumulation of soot and debris on the SHE surfaces
- Operating conditions: Exhaust gas temperature and flow rate
- Maintenance practices: Cleaning and inspection schedules
- A study of a tubular SHE in a steel mill furnace showed a 15% reduction in fuel consumption
- A plate-fin SHE installed in a glass furnace resulted in a 10% increase in furnace efficiency
- A regenerative SHE in a power plant furnace reduced emissions by 20%
- Advanced materials: Development of new materials with higher heat transfer rates and corrosion resistance
- Innovative designs: Optimization of airflow and heat transfer through novel designs
- Control systems: Integration of sensors and control systems to optimize SHE performance
Performance Evaluation of Secondary Heat Exchangers: A Furnace Equipped With A Secondary Heat Exchanger.

SHE performance is evaluated using metrics such as:
Factors affecting performance include:
Case Studies of Secondary Heat Exchangers in Furnaces
Case studies demonstrate the benefits of SHEs:
Future Trends in Secondary Heat Exchanger Technology
Emerging trends in SHE technology include:
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of a secondary heat exchanger in a furnace?
To capture additional heat from the exhaust gases, improving overall furnace efficiency.
What factors influence the design of a secondary heat exchanger?
Material selection, size, shape, airflow optimization, and heat transfer efficiency.
What are the common types of secondary heat exchangers used in furnaces?
Tubular, plate-fin, and spiral.