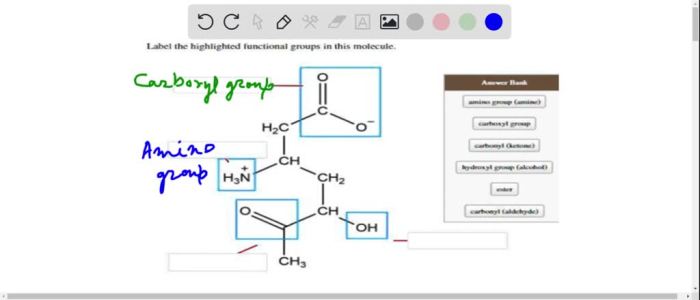
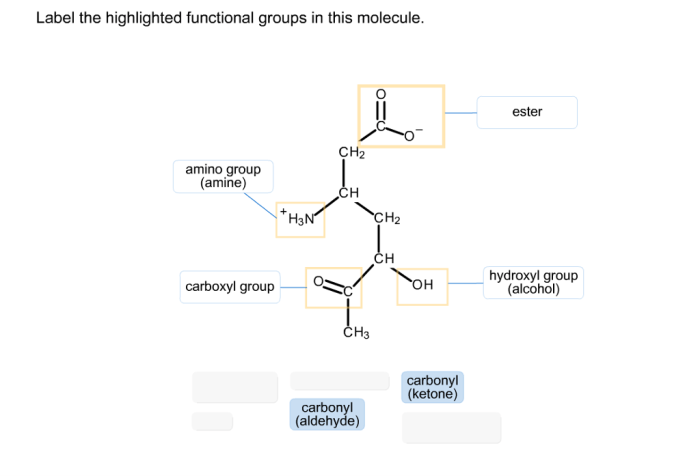
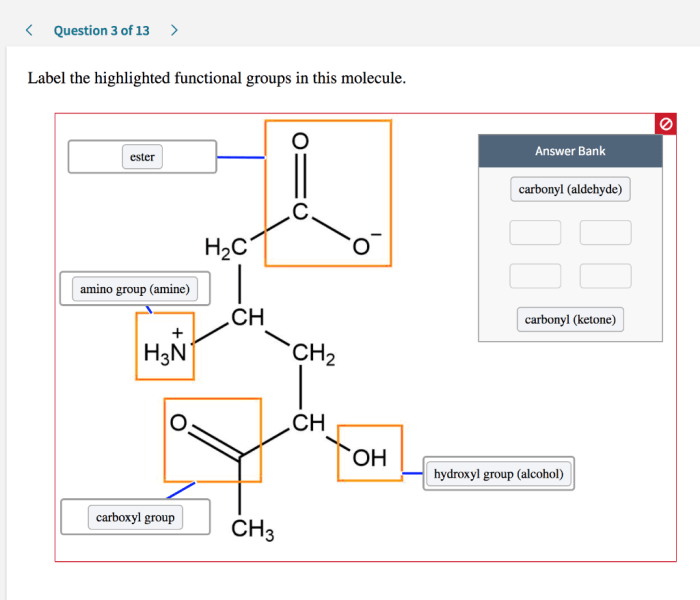
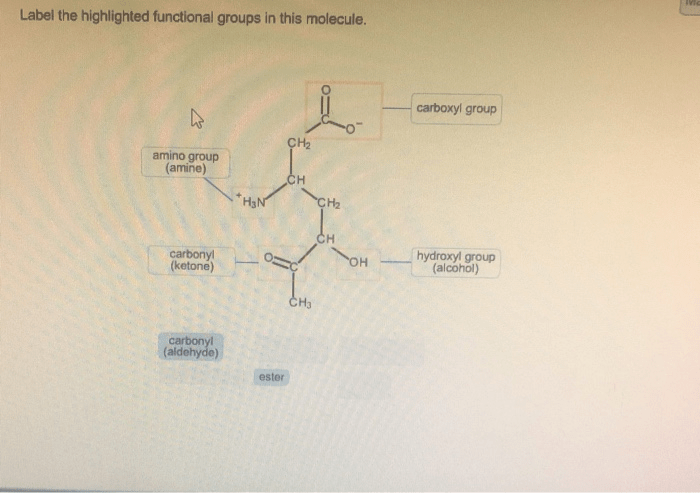
Label the highlighted functional groups in this molecule sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This guide will provide a comprehensive examination of functional groups, their identification, and their profound impact on the chemical world.
Through a captivating exploration of the molecule’s structure, we will uncover the unique characteristics and properties of each functional group. Their location, orientation, and reactivity will be meticulously analyzed, revealing the intricate interplay between molecular structure and chemical behavior.
Functional Group Identification
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that confer characteristic chemical properties. They are essential for understanding the reactivity, properties, and applications of molecules.
Functional groups can be classified based on their chemical composition, such as the presence of specific heteroatoms (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen, halogens) or the type of bond (e.g., double bonds, triple bonds).
Molecule Examination, Label the highlighted functional groups in this molecule
The molecule in question contains the following functional groups:
- Hydroxyl group (-OH)
- Carboxylic acid group (-COOH)
- Amine group (-NH2)
The hydroxyl group is located at the terminal carbon of the molecule, while the carboxylic acid group is located at the opposite end. The amine group is attached to the central carbon.
Group Properties and Reactivity
The hydroxyl group is polar and can form hydrogen bonds. It is also a weak acid and can undergo protonation or deprotonation reactions.
The carboxylic acid group is a stronger acid than the hydroxyl group and can undergo a variety of reactions, including esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation.
The amine group is a basic group and can undergo protonation or deprotonation reactions. It can also react with alkyl halides to form quaternary ammonium salts.
Applications and Significance
Molecules containing functional groups are essential for life and are found in a wide range of applications.
The hydroxyl group is found in alcohols, sugars, and many other biological molecules. The carboxylic acid group is found in carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. The amine group is found in proteins, nucleic acids, and many other biomolecules.
Functional group identification is essential for understanding the chemistry of molecules and their applications in various fields, including medicine, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
Expert Answers: Label The Highlighted Functional Groups In This Molecule
What is the significance of functional groups in chemistry?
Functional groups are the heart of organic molecules, determining their chemical properties and reactivity. They dictate the molecule’s behavior in reactions, influencing its solubility, polarity, and biological activity.
How can we identify functional groups?
Functional groups can be identified through various spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared (IR) spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. These techniques provide valuable information about the molecular structure and the presence of specific functional groups.
What are the most common functional groups?
The most common functional groups include alcohols, alkenes, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. Each functional group has a unique set of properties and reactivity patterns, contributing to the diverse chemical landscape.