Biochemical tests for food macromolecules labster – In the realm of food analysis, biochemical tests for food macromolecules take center stage as indispensable tools for deciphering the intricate composition of our sustenance. These tests empower us to unravel the secrets of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, revealing their presence, quantity, and quality.
The Labster virtual lab simulation provides an immersive platform to delve into the intricacies of biochemical testing, offering a hands-on experience that illuminates the principles and applications of these vital techniques.
1. Introduction: Biochemical Tests For Food Macromolecules Labster
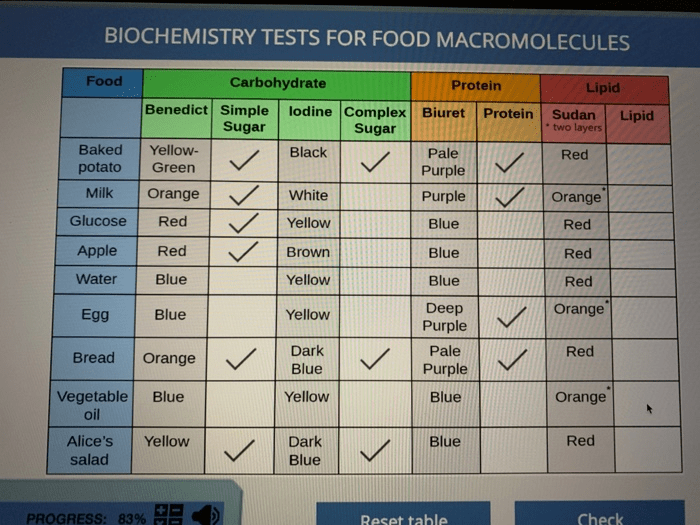
Biochemical tests are analytical procedures used to identify and quantify specific chemical compounds or macromolecules in food samples. These tests play a crucial role in food analysis, providing valuable information for quality control, safety assessment, and nutritional evaluation.
The Labster virtual lab simulation is designed to provide students with hands-on experience in conducting biochemical tests for food macromolecules. Through interactive simulations, students can learn the principles and procedures involved in these tests, and gain a deeper understanding of the chemical composition of food.
2. Types of Biochemical Tests

2.1 Carbohydrate Tests
- Benedict’s test: Detects reducing sugars based on the reduction of cupric ions to cuprous ions, resulting in a color change.
- Iodine test: Identifies starch and glycogen based on the formation of a blue-black complex.
- Molisch test: A general test for carbohydrates based on the dehydration of carbohydrates to furfural, which reacts with α-naphthol to produce a purple color.
2.2 Protein Tests
- Biuret test: Detects proteins based on the formation of a purple complex between peptide bonds and cupric ions.
- Ninhydrin test: Detects amino acids and proteins based on the formation of a blue or purple color when reacted with ninhydrin.
- Xanthoproteic test: Identifies proteins based on the formation of a yellow color when reacted with concentrated nitric acid.
2.3 Lipid Tests, Biochemical tests for food macromolecules labster
- Sudan IV test: Detects lipids based on their solubility in organic solvents and their ability to stain lipid droplets.
- Oil Red O test: A specific test for triglycerides based on their ability to stain lipid droplets.
3. Procedures for Biochemical Tests

The general procedures for conducting biochemical tests involve the following steps:
- Sample preparation: Prepare the food sample according to the specific test requirements, such as homogenization, extraction, or filtration.
- Reagent addition: Add the appropriate reagent to the sample, which reacts with the target macromolecule.
- Incubation: Allow the reaction to proceed for a specified time and temperature.
- Observation of results: Observe the physical or chemical changes that occur, such as color change, precipitate formation, or gas evolution.
4. Interpretation of Results
The results of biochemical tests are interpreted based on the observed changes. A positive result indicates the presence of the target macromolecule, while a negative result indicates its absence.
The intensity of the reaction can provide an indication of the concentration of the macromolecule. For example, a strong positive result may indicate a high concentration, while a weak positive result may indicate a low concentration.
5. Applications of Biochemical Tests
Biochemical tests are widely used in food analysis for various purposes, including:
- Quality control: Assessing the nutritional content and sensory properties of food products.
- Safety assessment: Detecting the presence of contaminants, such as bacteria, toxins, or pesticides.
- Nutritional evaluation: Determining the macronutrient and micronutrient content of food products.
These tests are essential for ensuring the safety, quality, and nutritional value of food products.
6. Limitations and Considerations
Biochemical tests have certain limitations and factors that can affect their accuracy and reliability, including:
- Specificity: Some tests may not be specific for a particular macromolecule and may react with other compounds.
- Sensitivity: Some tests may not be sensitive enough to detect low concentrations of the target macromolecule.
- Interfering substances: Other compounds present in the food sample may interfere with the test results.
To address these limitations, it is important to use validated test methods, consider the specificity and sensitivity of the tests, and perform multiple tests to confirm the results.
Q&A
What is the significance of biochemical tests in food analysis?
Biochemical tests play a crucial role in food analysis by identifying and quantifying specific macromolecules, providing insights into the nutritional content, quality, and safety of food products.
How does the Labster virtual lab simulation enhance the learning experience?
The Labster virtual lab simulation offers an interactive and engaging platform for students to explore biochemical tests, allowing them to visualize and manipulate experimental procedures, enhancing their understanding of the principles and applications of these techniques.
What are the limitations of biochemical tests?
While biochemical tests are powerful tools, they have certain limitations, such as potential interference from other substances, accuracy constraints, and the need for skilled personnel to interpret results.