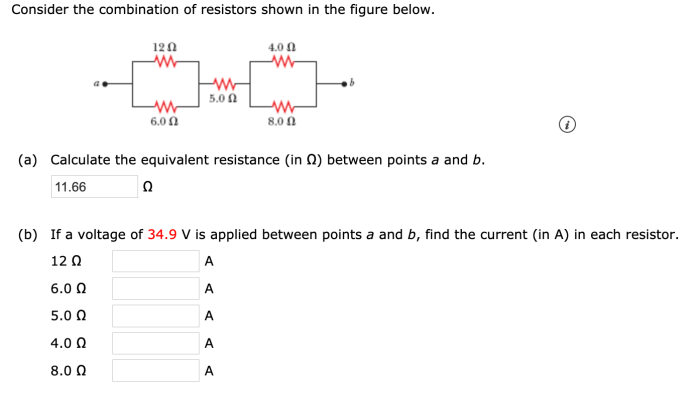
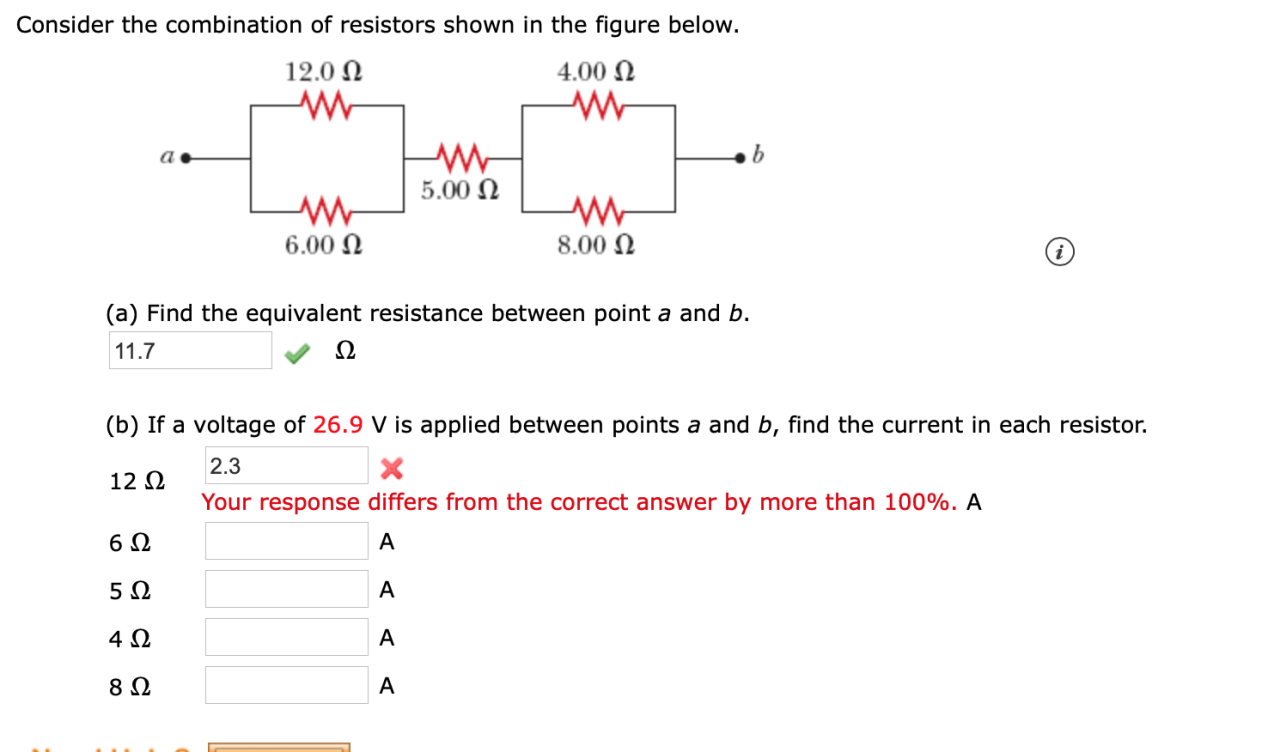
Consider the combination of resistors shown in the figure below. The topic at hand delves into the realm of electrical circuits, where resistors play a crucial role in controlling the flow of current and voltage. This exploration will uncover the intricacies of resistor types, their impact on total resistance, and practical applications in real-world scenarios.
As we embark on this journey, we will unravel the concepts of series and parallel circuits, empowering us to calculate the total resistance of resistor combinations with precision. Through a comprehensive analysis, we will dissect the effects of different resistor combinations, unlocking insights into their behavior and functionality.
Identify Resistor Types and Values
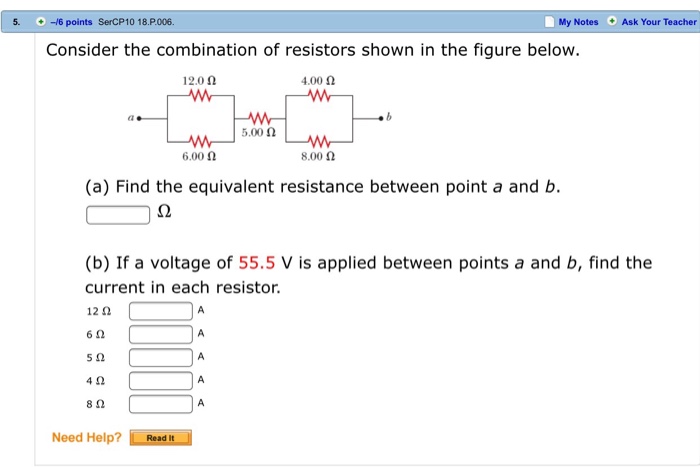
Resistors are passive electrical components that resist the flow of current. They are used to control the voltage and current in a circuit. Resistors can be classified by their type and value.The following table lists the resistors used in the figure, along with their resistance values, units, and color codes:
| Resistor Label | Resistance Value | Unit | Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 100 | Ω | Brown, Black, Brown |
| R2 | 220 | Ω | Red, Red, Brown |
| R3 | 330 | Ω | Orange, Orange, Brown |
| R4 | 470 | Ω | Yellow, Violet, Brown |
Frequently Asked Questions: Consider The Combination Of Resistors Shown In The Figure Below.
What factors influence the total resistance of a resistor combination?
The total resistance is affected by the resistance values of individual resistors and the way they are connected (series or parallel).
How can I calculate the total resistance of a series resistor combination?
To calculate the total resistance of resistors in series, simply add their individual resistance values.
What is the advantage of using parallel resistor combinations?
Parallel resistor combinations allow for a lower overall resistance, which can increase current flow.