Embark on an enlightening journey with the Student Exploration Building Topographic Maps Answer Key PDF, a comprehensive resource that empowers students to decipher the intricacies of topographic maps and unlock the secrets of Earth’s terrain. This guide unravels the fundamental concepts, key features, and practical applications of topographic maps, fostering a deeper understanding of our planet’s diverse landscapes.
Delving into the intricacies of topographic maps, this guide explores their construction techniques, utilizing field surveys and remote sensing technologies. It sheds light on the challenges and limitations inherent in map creation, providing a well-rounded perspective on the complexities involved.
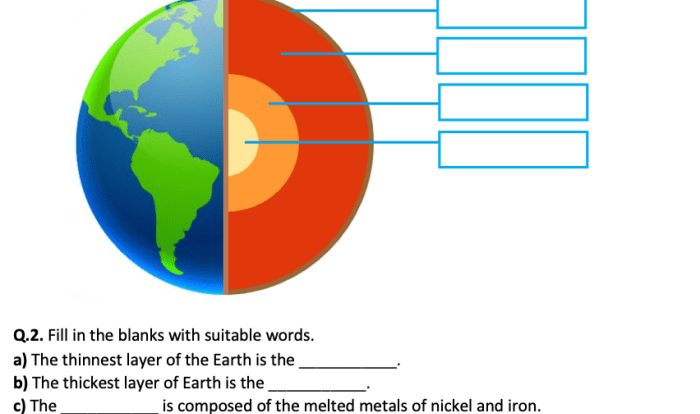
Topographic Maps: Student Exploration Building Topographic Maps Answer Key Pdf
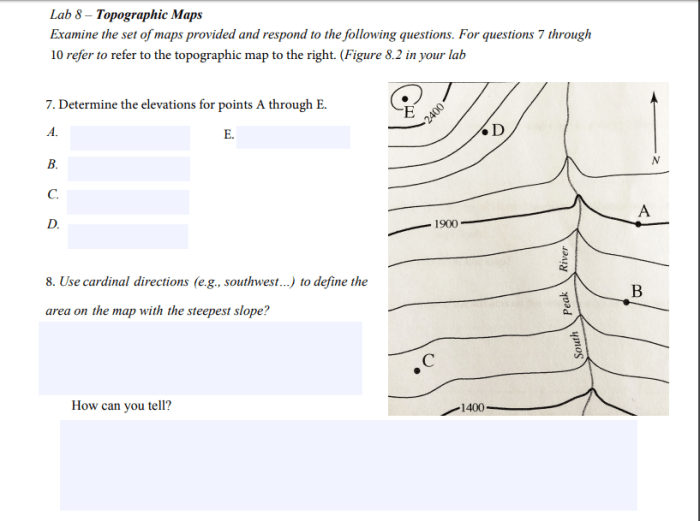
Topographic maps are specialized maps that depict the physical features of the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of elevation, terrain, and other geographic information.
Topographic maps are used in a wide range of fields, including geology, surveying, engineering, and environmental planning. They can be used to identify potential building sites, plan hiking trails, and assess the impact of natural disasters.
Key Features of Topographic Maps, Student exploration building topographic maps answer key pdf
- Contour lines: Lines that connect points of equal elevation.
- Elevation markers: Numbers that indicate the height of a specific point above sea level.
- Map scales: The ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
Contour lines are the most important feature of topographic maps. They allow users to visualize the shape and elevation of the land. By understanding how to interpret contour lines, users can determine the slope, steepness, and overall topography of an area.
Building Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are created using data from field surveys and remote sensing techniques. Field surveys involve measuring the elevation of points on the ground using instruments such as levels and theodolites.
Remote sensing techniques, such as photogrammetry and lidar, use aerial photography and lasers to create digital elevation models (DEMs). DEMs are then used to generate topographic maps.
Student Exploration Activities
Topographic maps can be used as a valuable tool for teaching students about geography and earth science. There are a number of engaging activities that can be used to help students develop their spatial reasoning skills and learn how to interpret topographic maps.
- Have students create their own topographic maps using data from field surveys or online resources.
- Use topographic maps to plan hiking trails or identify potential building sites.
- Analyze topographic maps to assess the impact of natural disasters, such as floods or landslides.
Additional Resources
- Interactive topographic maps: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/topographic-map/
- Educational videos on topographic maps: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a_Xgdm03YBE
- Downloadable topographic map data and software: https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/national-geospatial-program/national-map
FAQs
What are the key features of topographic maps?
Topographic maps are characterized by contour lines, elevation markers, and map scales. Contour lines represent elevation, while elevation markers provide specific height values. Map scales indicate the relationship between the map and the actual terrain.
How are topographic maps used in various fields?
Topographic maps find applications in diverse fields, including geology, engineering, urban planning, and recreation. Geologists use them to study geological formations, engineers to plan infrastructure projects, urban planners to design cities, and hikers to navigate trails.
What are the challenges in building topographic maps?
Building topographic maps involves challenges such as data accuracy, terrain complexity, and accessibility. Data accuracy can be affected by factors like measurement errors and data interpolation. Complex terrain can make it difficult to accurately represent elevation changes. Accessibility issues may arise in remote or hazardous areas.