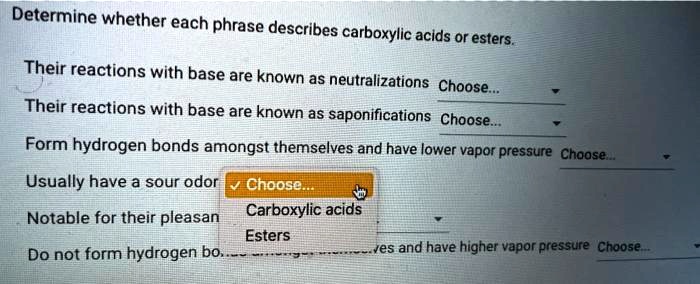
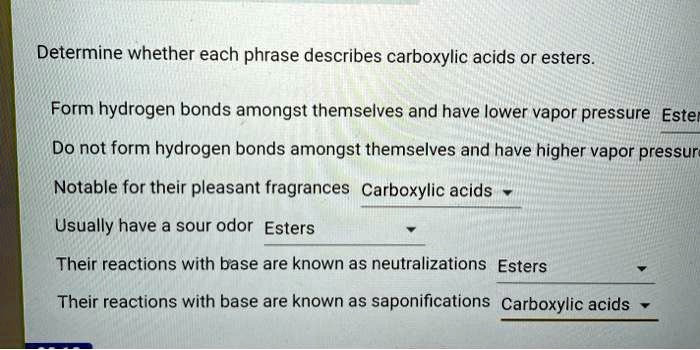
Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, we embark on a journey to determine whether each phrase describes carboxylic acids or esters. These two functional groups, despite sharing similarities, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. This comprehensive guide will provide a thorough understanding of their chemical structures, properties, reactions, uses, and identification methods, empowering you to confidently navigate the complexities of these essential compounds.
Carboxylic acids and esters play pivotal roles in various scientific disciplines and everyday applications. Understanding their unique properties and reactivity is crucial for comprehending their behavior in different chemical environments. Whether you are a student seeking to deepen your knowledge or a professional seeking to enhance your expertise, this guide will serve as an invaluable resource.
Definition

Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). The carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). Esters are organic compounds that contain an ester group (-COOR).
The ester group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to an alkyl or aryl group (-R).
Properties
Carboxylic acids and esters have different physical properties. Carboxylic acids are typically polar, high-boiling liquids or solids. Esters are typically nonpolar, low-boiling liquids or solids. The solubility of carboxylic acids and esters in water depends on the length of the carbon chain.
Carboxylic acids with short carbon chains are soluble in water, while carboxylic acids with long carbon chains are insoluble in water. Esters with short carbon chains are soluble in water, while esters with long carbon chains are insoluble in water.
| Property | Carboxylic Acids | Esters |
|---|---|---|
| Physical state | Liquid or solid | Liquid or solid |
| Polarity | Polar | Nonpolar |
| Boiling point | High | Low |
| Melting point | High | Low |
| Solubility in water | Depends on carbon chain length | Depends on carbon chain length |
Reactions: Determine Whether Each Phrase Describes Carboxylic Acids Or Esters
Carboxylic acids and esters undergo different reactions. Carboxylic acids react with bases to form salts. Carboxylic acids also react with alcohols to form esters. Carboxylic acids can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols. Esters react with water to form carboxylic acids and alcohols.
Esters also react with bases to form salts. Esters can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols.
Uses
Carboxylic acids and esters have a variety of uses. Carboxylic acids are used in the production of plastics, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Esters are used in the production of perfumes, flavors, and solvents.
| Compound | Uses |
|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids | Plastics, dyes, pharmaceuticals |
| Esters | Perfumes, flavors, solvents |
Identification
Carboxylic acids and esters can be identified by their physical properties and chemical reactions. Carboxylic acids are typically polar, high-boiling liquids or solids. Esters are typically nonpolar, low-boiling liquids or solids. Carboxylic acids react with bases to form salts. Carboxylic acids also react with alcohols to form esters.
Esters react with water to form carboxylic acids and alcohols.
| Property | Carboxylic Acids | Esters |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility in water | Depends on carbon chain length | Depends on carbon chain length |
| Odor | Pungent | Fruity |
| Reactivity | React with bases to form salts | React with water to form carboxylic acids and alcohols |
Questions and Answers
What is the key difference between carboxylic acids and esters?
Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters have an ester group (-COOR), where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
How can you identify carboxylic acids based on their physical properties?
Carboxylic acids typically have higher boiling points and melting points compared to esters due to stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
What are some common reactions of carboxylic acids?
Carboxylic acids undergo reactions with bases, alcohols, and reducing agents, forming salts, esters, and aldehydes or ketones, respectively.